From scribbled sketches to stunning renders on the screen: How 3D modeling and rendering bring ideas to life.
In today’s digital world, the ability to transform ideas into lifelike visuals is more important than ever. When combined, 3D modeling and rendering do just that – they create immersive visuals that captivate the eye and tell powerful stories. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of 3D modeling and rendering, answering key questions about what they are, how they work, how they differ, their applications, and what the future has in store for these processes. So let's just jump right in.

What is 3D modeling?
3D modeling is the process of creating a digital object in a virtual space. Like sculpting, you’re creating a three-dimensional digital representation of something, but instead of clay, you're using specialized software. In essence, it’s like sculpting with digital tools.
Types of 3D modeling and its applications
There are several types of 3D modeling. Let's explore them below.
- Polygonal modeling
Polygonal modeling involves building objects using polygons, which are flat shapes with three or more sides and hard edges. You can think of it like building something out of Legos. Each Lego brick is a polygon, and you put them together to create the overall shape. Polygonal modeling is particularly useful for visualizations, where large, detailed environments like architectural spaces need to be created quickly.
- NURBS modeling
For objects with smooth curves, like cars, handheld devices, or various mechanical parts, you would use NURBS modeling. NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) is a way of creating smooth-flowing surfaces using mathematical curves. To picture it better, just imagine bending a thin sheet of metal into any organic shape— that’s the power of NURBS.
- Subdivision surface modeling
Like NURBS, subdivision surface modeling is often used to create smooth, organic shapes such as characters or vehicle bodies. The main difference is that subdivision surface smooths shapes by subdividing polygons for organic forms, while NURBS uses mathematical curves for precise, smooth surfaces in hard-surface designs.
- Digital sculpting
For modeling super realistic characters, or specialized architectural features such as detailed facades, or intricate ornamental designs, you would use digital sculpting. You use digital tools to shape and mold the virtual model, adding details like wrinkles and pores in a character, or use a V-Ray wood material to model scratches and wear in a wooden cabinet.
- BIM
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is used in architecture, engineering, and construction. It focuses on creating a detailed, data-rich 3D model of a building or infrastructure project. It is especially useful for collaborative construction projects as it integrates data like materials, cost estimates, and project timelines, into the design.
- Procedural and Parametric Modeling
Procedural and parametric modeling combine algorithms, rules, and parameters to generate objects and environments, rather than relying on manual creation. Procedural modeling is ideal for large-scale environments like cities or terrain, often used in game design and film production, while parametric modeling creates objects based on adjustable constraints, such as building height or gear radius, making it perfect for architecture and product design where flexibility and easy modifications are key.
- Volumetric modeling
Volumetric modeling is used to create 3D models that represent volumes, such as smoke, fog, clouds, or liquids, and is commonly used in simulations and visual effects for movies and video games. Chaos Phoenix offers an easier, more dynamic approach than traditional modeling by simulating these effects in real-time, allowing for customizable and realistic results without pre-modeled assets.
- 3D scanning
3D scanning involves capturing real-world objects or environments using a 3D scanner, which creates a digital model based on the shape, size, and texture of the scanned object. This method is commonly used in industries like architecture, heritage preservation, and manufacturing for quickly creating accurate digital replicas of physical objects or spaces.
Popular 3D modeling software
- For animation and character design
Autodesk Maya is known for its strengths in animation and character design, seamlessly integrating with V-Ray for cinematic visuals, while Cinema 4D is popular for motion graphics and 3D modeling, also integrating with V-Ray for detailed animation rendering.
- For architectural visualization and design
Autodesk 3ds Max is a favorite for 3d modeling in architectural visualization and product design, heavily integrated with V-Ray for photorealistic images.
SketchUp, widely used in architecture and interior design, supports both V-Ray and Enscape for intuitive, real-time, and photorealistic rendering.
Revit, commonly used in architectural design and BIM (Building Information Modeling), is compatible with both Enscape and V-Ray for visualization, while Archicad and Vectorworks, also favored by architects, are supported by Enscape for real-time rendering and walkthroughs.
Rhinoceros (Rhino) is ideal for industrial and architectural design, with V-Ray for detailed rendering and Enscape for real-time visualization.
Archicad and Vectorwarks are useful for 2D and 3D drafting, parametric modelling, BIM and are both compatible with Enscape.

What is 3D rendering?
While 3D modeling involves sculpting a three-dimensional object in a virtual space, rendering is the process of taking that 3D model and making it look real. It’s where lighting, textures and everything else come in to bring a photoreal look. Rendering is all about simulating how light interacts with the 3D model to create a 2D image or an animation. It's basically like taking a picture of your 3D model.
Types of 3D rendering
Real-time rendering allows for smooth exploration of scenes, making it easy to move and interact with them. Photorealistic rendering focuses on achieving a high level of realism, commonly seen in architectural visualization. Stylized rendering, on the other hand, produces artistic effects such as cartoons or sketches.
Applications
Whether for realistic environments, interactive designs, or artistic visuals, each rendering style plays a key role in enhancing media and design across various industries including VFX rendering for film and TV, architectural visualization, and product design by creating lifelike visuals, immersive experiences, lifestyle images, and engaging digital content.
Clients can provide more informed feedback when shown 3D images instead of 2D plans.
Because they can visualize the project clearly. They don't know how to read and interpret 2D plans. But they can understand a 3D image.
Virtual walkthroughs created from 3D models help to show clients and stakeholders how a future space will look and function. Once the 3D model is ready, rendering tools such as Enscape can provide a realistic walkthrough that clients can even navigate themselves, allowing them to really engage with the design.
Interior designers often utilize 3D modeling to experiment with different layouts, materials, and lighting options before construction.
3D rendering is essential for marketing and presentations in real estate. Architectural animations can showcase a project, and photorealistic images clearly show how a building or space will look like in reality. Helping to communicate to potential buyers what their new potential home would feel and be like to live in.
Different types of 3D rendering software
V-Ray is a powerful 3d rendering software that enables AEC (Architecture, Engineering, and Construction) professionals to create high-quality, photorealistic visuals of architectural designs, engineering projects, and construction simulations. It is also widely used by M&E (Media and Entertainment) professionals for VFX, animations, and cinematic visuals. Discover how V-Ray can help you visualize anything imaginable.
Enscape is a real-time visualization and virtual reality plug-in that empowers architecture and design workflows, offering seamless integration with the most widely used CAD and BIM tools in the AEC industry. It is ideal for immersive, real-time walkthroughs of architectural models and design concepts.
Chaos Corona is an intuitive render engine tailored to the archviz community. While also popular in automotive and product visualization, its user interface, feature set, and pricing are optimized for the needs of architectural visualizers. Now part of the Chaos ecosystem, Corona benefits from access to a range of industry-standard tools developed by Chaos.

Rendering vs. 3D modeling: key differences
Output differences
In terms of output, 3D modeling results in a digital 3D model, while rendering generates 2D images or animations that represent the model in a visually compelling way.
Tools and software
3D modeling uses software like Blender, Maya, ZBrush, or 3ds Max. Rendering relies on rendering engines such as V-Ray, Enscape, or Chaos Corona to create photorealistic or stylized outputs.
Hardware demands
3D modeling is generally less hardware-intensive, though complex scenes can still demand high-performance setups. Rendering requires significant computing power, especially for high-resolution, photorealistic results. GPU and CPU performance play a critical role.
Creativity vs. technicality
Modeling is more creative and design-oriented, whereas rendering involves technical skills to achieve realism or desired visual effects. For instance, mastering techniques like those outlined in 11 lighting rendering tips to boost photorealism.
Skill sets
Modeling requires a lot of spatial awareness and an understanding of form and proportion. You have to be able to visualize the object in your mind and then translate that into a 3D model. It's like being a sculptor but in a digital world using software tools to sculpt your model. Rendering on the other hand, is more about better understanding light and color and how to create realistic looking materials and textures, so it's more like being a painter or photographer.
Team collaboration
In 3D modeling, collaboration typically involves working closely with designers, architects, or concept artists to refine the base structure of the model and ensure it aligns with the project’s vision. This stage emphasizes iterative feedback to perfect the form and geometry. In the 3d rendering processes however, teamwork often shifts toward collaborating with art directors, visual effects supervisors, or clients to finalize the scene’s visual style, realism, and overall presentation. Both stages require effective communication, but the focus of collaboration changes as the project progresses.
Time management
The time investment in 3D modeling is largely focused on refining the details and process of creating the object and ensuring that its topology is clean and optimized for any further rendering and use. This stage requires precision and iteration to achieve a well-constructed model. Rendering, on the other hand, often involves longer periods spent fine-tuning lighting, materials, and other settings, as well as waiting for the actual rendering process to complete. Additional time may also be required for post-production work to enhance the final output.
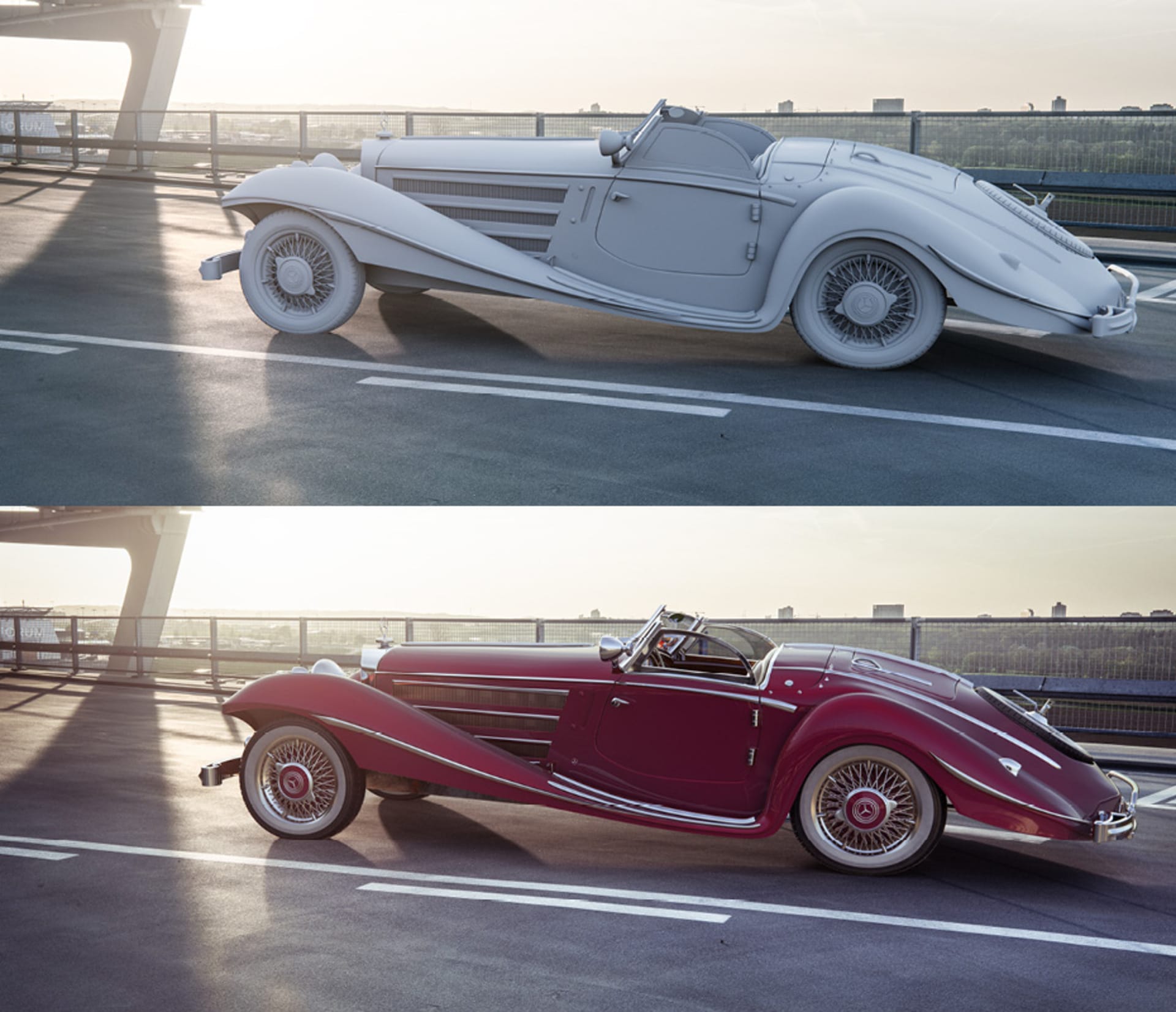

The 3D modeling and rendering process
The 3D modeling process
The 3D modeling process generally begins with concept creation, where you come up with the idea for the project, sketch it out, and then you move on to the modeling phase where you create a 3D model. After that, texturing and rigging follow. Texturing is the process of adding colors and patterns to the 3D model. And rigging is the process of creating a skeleton for a model so it can be animated. After that, it's on to rendering. There are a lot of variations depending on the project and it's a flexible process that can be adapted to different needs of the specific project or the artist’s approach.
The 3D rendering process
Once the model is complete, the 3D rendering process begins. This typically starts with setting up textures, shaders, and lighting to bring the model to life. The scene is then rendered to produce the final image or animation. Finally, post-processing enhancements, such as adding effects are applied to improve realism and visual appeal. Again, this can vary depending on the requirements of the project.
Workflow tips
It goes without saying that you should first have the right hardware to get you started with rendering. Check out how to build your best computer for rendering for some helpful tips. For large projects, consider optimizing your workflow by leveraging render farms to handle the heavy computational load. To improve efficiency while building out your scene, you should make use of asset libraries like Chaos Cosmos, which offer a wide range of smart ready-to-use models.
Benefits of combining 3D modeling and rendering
When combined, 3D modeling and rendering are used to create visually compelling images and animations that leave a lasting impact. This combination is essential for applications in VR/AR, where immersive experiences are key, and in advertising, where high-quality visuals can capture audience attention. Real-world examples of this synergy can be seen in architectural visualization, where architectural rendering software helps bring designs to life, and in product marketing, where 3D models are used in product design and e-commerce to enhance customer engagement.
3D models can be reused in different renders to create unique images without additional modeling. For example, you can add different materials, assets, lighting, and weather conditions to a render to create different looks. It's the same model, but you can add different effects and assets in the rendering tool.
Tips for effective 3D modeling and rendering
Boost productivity by using plugins like Chaos Cosmos or utilizing GPU rendering for faster processing times. Incorporating lighting techniques such as HDRi lighting can dramatically enhance realism, while asset libraries like Quixel Megascans provide high-quality options that save both time and effort in the modeling and rendering process.

Common challenges in 3D modeling and rendering
Technical challenges
One of the main challenges in 3D modeling and rendering is managing complex models, which can become difficult to manipulate and render efficiently. Achieving realistic lighting for accurate models is another challenge, as it requires precise adjustments to simulate natural and artificial light sources convincingly. Additionally, working with limited hardware can hinder the rendering process, as it may struggle to handle the large amounts of data and the high computational power needed for detailed models and realistic renders.
Creative challenges
Creatively, 3D artists face the challenge of maintaining a balance between realism and artistic vision. Ensuring that materials and textures appear natural yet stylized enough to fit the desired aesthetic can require extensive trial and error. Similarly, modeling demands a strong understanding of form, proportion, and scale to create realistic images of objects and environments that feel both cohesive and functional. Bridging the gap between technical limitations and artistic aspirations often requires creative problem-solving, such as using smart design techniques to create accurate models or optimizing models for better performance without sacrificing detail.
Troubleshooting tips
To reduce render noise, optimize your settings, ensuring smoother and cleaner outputs. For example, learn how to create noise-free images with V-Ray for 3ds Max. Simplifying complex models can also improve performance, making the rendering process faster and more efficient. For handling large files, consider using render farms, which can significantly speed up the rendering of resource-intensive projects. Additionally, building the right computer for rendering can provide the necessary power to tackle demanding tasks with ease.
The future of 3D modeling and rendering
AI and Automation
AI and automation are streamlining workflows in 3D modeling and rendering by handling tasks like UV unwrapping, procedural modeling, and noise reduction. AI will take over more of the technical tasks involved in 3D modeling and rendering which in effect is going to free up artists and designers to focus on the more creative aspects of their work. As AI evolves, it will make high-quality results more accessible to users of all skill levels.
Cloud and real-time rendering
Cloud rendering removes the need for expensive hardware by processing complex scenes remotely, making collaboration and sharing easier. With cloud-based solutions like Chaos Cloud, rendering power can be scaled on-demand, allowing studios and freelancers to tackle projects that were once limited by local resources. Real-time rendering, powered by advanced GPUs and optimized engines like Enscape and Vantage, offers immediate feedback that accelerates the design process and enables interactive visualization. This allows artists, designers, and architects to seamlessly explore and interact with large, highly detailed, photorealistic 3D environments in real-time, enhancing their ability to make quick, informed decisions during the creative process.
The rise of immersive 3D content
The growth of virtual worlds and the metaverse is driving demand for immersive 3D content. Industries are pushing for more realistic images and interactive environments, inspiring innovation in techniques like virtual reality integration and dynamic rendering for richer digital experiences.

To wrap up
3D modeling and rendering, while distinct processes, are deeply interconnected and essential for producing high-quality visuals. By combining modeling and 3D rendering techniques with powerful rendering technologies, artists are able to achieve impactful, immersive, and visually compelling results across industries.
If this deep dive has sparked your curiosity, don't hesitate to jump in and start exploring. Experiment with different software, connect with the expert 3D rendering community, and let your imagination run wild. Happy rendering!